![]()
Pros and cons of PCB router machines
Precision Perfected: Mastering PCB Milling and Routing for Flawless Circuit Boards
As someone who’s been in the trenches of pcb manufacturing for over two decades – as a PCB Router Machine, a PCB Laser Depaneling expert, and even intimately familiar with the nuances of V-Groove Depaneling, PCB/FPC Punching Machine operations, and the integration of Automatic Equipment and essential Accessories – I’ve seen firsthand the evolution of pcb mill technology. This isn’t just an article; it’s a deep dive born from years of experience, guiding you through the intricate world of pcb router and cnc machine technology to help you achieve impeccable printed circuit board production. If you’re involved in pcb design, small cnc operations, or are exploring the best methods for milling pcbs or understanding the difference between milling or routing, you’ve come to the right place. We’ll explore the critical questions and solutions, ensuring your journey in circuit boards and printed circuit fabrication is smooth and successful.
Article Outline: Your Roadmap to PCB Milling Mastery
Here’s what we’ll be covering in this comprehensive guide to pcb milling and routing:
- What exactly is a PCB Mill or PCB Router Machine and how does it differ from other cnc machine types?
- Why choose pcb milling process over traditional etch methods for your circuit boards?
- What are the key components of a pcb router and how do they impact pcb fabrication?
- How do you prepare your pcb design files (like gerber files) for the milling process using software like FlatCAM?
- What considerations are crucial when selecting milling bit and drill bit for your pcbs?
- How do you execute the pcb milling process, including setting feed rates and milling depth?
- What are the best practices for drilling drill holes and achieving accurate edge cut on your pcb board?
- What are the advantages of using a cnc machine for creating custom circuit boards compared to other fabrication methods?
- From prototyping to production: When is pcb milling process the ideal solution for your pcb production needs?
- What future innovations are on the horizon for pcb router technology, and how can they benefit your pcb assembly process?
Delving into the World of PCB Milling and Routing
1. What exactly is a PCB Mill or PCB Router Machine and how does it differ from other cnc machine types?
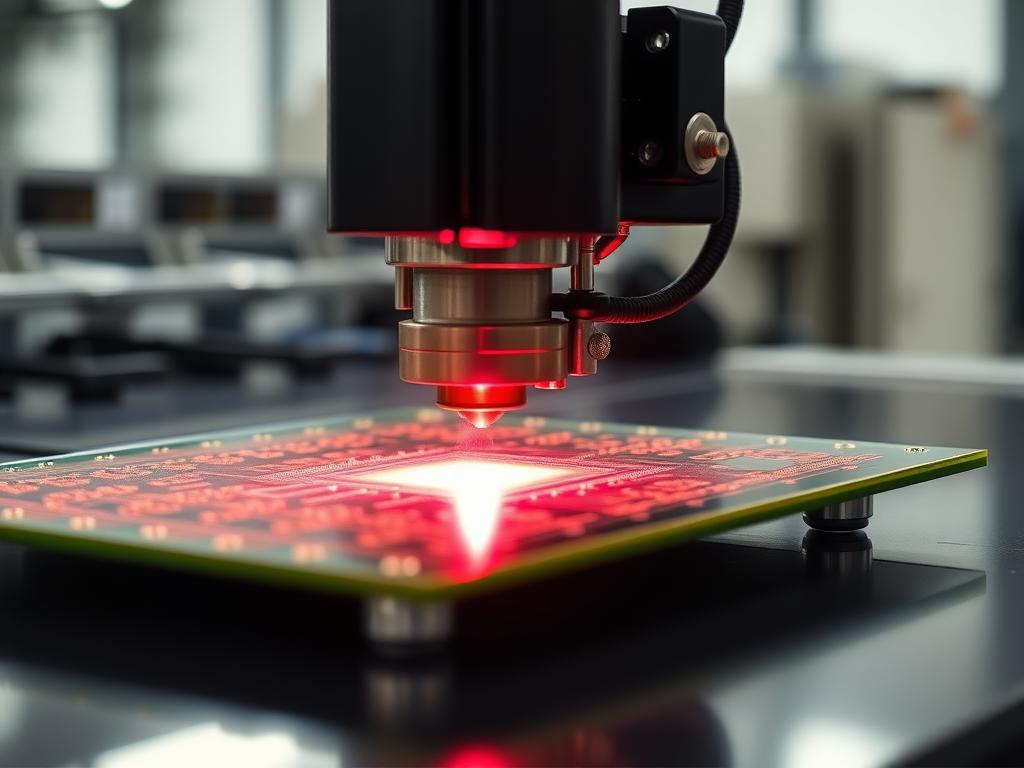
As a PCB Router Machine, I can tell you firsthand that my primary function is the precise removal of material from a pcb board to create the desired electrical circuits. Think of it as a specialized cnc machine meticulously carving out the conductive pathways, isolating pads, and shaping the board’s edges. While sharing the core principles of cnc machining – controlled movement along multiple axes (x and y axes, and often a z axis) guided by computer numerical control (cnc) – a pcb mill is specifically designed for the delicate work required for printed circuit boards. Unlike general-purpose milling machines that might work with metal or wood, our focus is on materials like FR4, copper, and sometimes flexible substrates. This often involves higher spindle speeds and finer tolerance capabilities to accurately create the intricate traces and pads essential for modern electronics.
2. Why choose pcb milling process over traditional etch methods for your circuit boards?
Having witnessed the evolution of pcb fabrication, I can confidently say that pcb milling process offers compelling advantages, especially for prototyping and low-volume production. Traditional etch methods involve chemical etching, using etchants like ferric chloride or ammonium persulfate to remove copper. While effective for mass production, this process can be time-consuming, involve hazardous chemicals, and require careful disposal. In contrast, milling provides a faster turnaround for design iterations. As a PCB/FPC Punching Machine and having seen the precision offered by PCB Laser Depaneling, I appreciate the clean, dry process of milling, which avoids the mess and environmental concerns of chemical etch. It’s also ideal for creating double sided boards and even intricate multi-layer designs without the complexities of chemical registration. For those who need a pcb quickly to test a board design, milling provides that agility.
3. What are the key components of a pcb router and how do they impact pcb fabrication?
As a PCB Router Machine, my core lies in several key components working in harmony. The high-speed spindle is the heart, holding the milling bit or drill bit and spinning it at thousands of RPMs to precisely cut the copper layer. The gantry system, often utilizing precise linear bearing and ball bearings, ensures smooth and accurate movement of the spindle across the pcb board. A robust clamp system is vital to securely hold the substrate during the milling operation, preventing unwanted movement that could compromise accuracy. The cnc firmware interprets the design files and directs the stepper motor controlling the gantry’s movement. Effective dust extraction is also a crucial, often overlooked, component for maintaining a clean work environment and ensuring clear visibility during the milling process. Each of these elements contributes to the final quality and precision of the routed pcb.
4. How do you prepare your pcb design files (like gerber files) for the milling process using software like FlatCAM?
The journey from pcb design to physical board requires translating your design into instructions a cnc machine can understand. Gerber files, the industry standard for pcb layout information, need to be processed by software like FlatCAM. FlatCAM allows you to import your gerber files and your drill file, representing the conductive layers, solder mask, and drill locations. You then define the cutting tool parameters, such as the diameter of the hole for drilling or the end mill size for routing. FlatCAM generates the milling paths or G-code, the numerical control language that guides the cnc machine. It’s crucial to accurately specify parameters like milling depth and milling depth per single pass to achieve the desired results and avoid damaging the substrate or the cutting tool. Understanding software like Kicad for pcb design and its compatibility with FlatCAM is essential for a seamless workflow.
5. What considerations are crucial when selecting milling bit and drill bit for your pcbs?
Choosing the right cutting tool is paramount for achieving good results in pcb work. As someone intimately familiar with the Accessories side of things, I can emphasize the importance of material, geometry, and size. For isolating traces and pads, small diameter milling bits are used, often carbide for durability. V-carve bits are excellent for creating isolation channels. For drill holes, selecting the correct drill bit size based on the vias and component lead sizes is crucial. High-speed steel (HSS) bits are suitable for some materials, but carbide bits offer superior lifespan and performance, especially for finer holes. Consider the copper layer thickness and the substrate material when selecting your bits. Using the wrong bit can lead to broken bits, poor cut quality, or damage to the pcb board.
6. How do you execute the pcb milling process, including setting feed rates and milling depth?
The execution phase requires careful attention to detail. Securely clamp the pcb board onto the machine bed. Load the generated G-code into the cnc controller. Setting the feed rates (the speed at which the cutting tool moves across the material) and milling depth (how deep the cutting tool cuts in each pass) are critical parameters. Too high a feed rate can cause the bit to break or chip the pcb board, while too low a rate can lead to excessive heat and wear on the bit. Similarly, the milling depth per pass needs to be appropriate for the material and cutting tool. Often, multiple passes at shallower depths are preferable to a deep single pass, especially for thicker copper or delicate structures. Always perform a test run on a scrap piece if you are unsure of the optimal settings.
7. What are the best practices for drilling drill holes and achieving accurate edge cut on your pcb board?
Drilling small holes accurately requires a stable machine, sharp drill bits, and appropriate feed rates. Ensure your drill bit is securely chucked and running true. For edge cut, which defines the final shape of your pcb board, a robust end mill designed for side-cutting is recommended. Program the milling paths for the edge cut carefully, often using an “outline” strategy. Consider leaving small tabs to hold the board in place during the milling process, which can be broken or cut away afterwards. Accurate edge cut is crucial for proper fitment in enclosures and for a professional finish. As a V-Groove Depaneling expert, I understand the importance of clean and precise separation, and the same principles apply to edge cut using a router.
8. What are the advantages of using a cnc machine for creating custom circuit boards compared to other fabrication methods?
As someone involved in various pcb manufacturing processes, including Automatic Equipment for handling and sorting, I see the distinct advantages of cnc milling for custom circuit boards. The speed and convenience for prototyping are unparalleled. You can go from design to a physical board in a matter of hours. The ability to easily iterate on designs without the delays and costs associated with chemical processing is a significant benefit, especially for hobbyists and small businesses. Furthermore, milling provides greater control over the milling process, allowing for intricate designs and the creation of features that might be difficult or impossible with chemical etching. For low to medium volume production, pcb milling offers a cost-effective and efficient solution.
9. From prototyping to production: When is pcb milling process the ideal solution for your pcb production needs?
While chemical etching remains the dominant method for mass production, pcb milling process shines in specific scenarios. For rapid prototyping and testing new pcb design concepts, milling provides an immediate feedback loop. For small production runs or custom circuit boards where flexibility and quick turnaround are paramount, it’s an excellent choice. Educational institutions and research labs often prefer milling due to its ease of use and safety compared to chemicals. If your designs require intricate features or you’re working with specialized materials where chemical processing is challenging, pcb milling would be a better fit. However, for very high-volume production, the scalability and cost-effectiveness of etching process generally outweigh the benefits of milling.
10. What future innovations are on the horizon for pcb router technology, and how can they benefit your pcb assembly process?
The field of pcb router technology is constantly evolving. We’re seeing advancements in spindle technology leading to higher speeds and improved precision. Integration with robotic arms and automated material handling systems, much like our Automatic Equipment, is streamlining the entire pcb assembly process. Improved cnc firmware and software are making the programming and operation of these machines use easier and more intuitive. Developments in multi-axis cnc machines allow for more complex 3D milling or routing of circuit boards. These innovations will lead to faster turnaround times, increased automation, and the ability to create even more sophisticated and compact electronic devices. Even the integration of PCB Laser Depaneling technology into hybrid systems could offer even greater flexibility in pcb production.
FAQs: Your Burning PCB Milling Questions Answered
What are the main advantages of using a pcb mill? The primary benefits include rapid prototyping, no harsh chemicals, ease of iteration, and the ability to create complex geometries.
Is pcb milling suitable for double-sided PCBs? Yes, with careful alignment and fixturing, double sided PCBs can be effectively milled.
What software is commonly used for generating G-code for pcb milling? FlatCAM is a popular open-source option, but other commercial software packages are also available.
How accurate are pcb milling machines? Modern pcb milling machines can achieve very high accuracy, often down to a few thousandths of an inch, depending on the machine and settings.
Can a pcb mill also be used for pcb drilling? Yes, most pcb mills are equipped with a spindle capable of holding drill bits for creating drill holes.
Key Takeaways: Mastering the Art of PCB Milling
- PCB milling is a versatile method for creating circuit boards, especially for prototyping and low-volume production.
- Understanding the components of a pcb router and their functions is crucial for successful pcb fabrication.
- Proper file preparation using software like FlatCAM is essential for generating accurate milling paths.
- Selecting the correct milling bit and drill bit is critical for achieving quality results.
- Careful execution, including setting appropriate feed rates and milling depth, is vital for preventing errors.
- PCB milling provides significant advantages over traditional etching for rapid prototyping and custom circuit boards.
- Future innovations in pcb router technology promise even greater efficiency and capabilities.
Ready to revolutionize your pcb production? As a leading manufacturer of PCB Router Machine, PCB Laser Depaneling, and V-Groove Depaneling solutions, we have the expertise and technology to meet your needs. Our products are trusted by industry giants like TP-LINK, Canon, BYD, Flex, TCL, Xiaomi, Lenovo, OPPO, HONOR, and Foxconn. Contact us today to explore how our advanced depaneling and milling solutions can elevate your electronic manufacturing processes. Let’s build the future of electronics together!
Learn more about our PCB Router Machines Explore our advanced PCB Laser Depaneling solutions Discover our precise V-Groove Depaneling options See our range of efficient PCB/FPC Punching Machines Automate your production with our Automatic Equipment Find the right Accessories for your depaneling needs