![]()

PCB depaneling for wearable devices
From Manual to Laser: A Deep Dive into PCB Depaneling Methods
As someone with over 20 years immersed in the PCB industry, I’ve seen firsthand the incredible evolution of PCB depaneling. From rudimentary manual methods to the precision of laser depaneling, the way we separate individual circuit boards has dramatically changed. This article isn’t just a technical overview; it’s a journey through the different approaches, highlighting the pros, cons, and why choosing the right method is crucial for efficient and high-quality PCB manufacturing. Whether you’re a seasoned engineer or a PCB enthusiast, understanding these nuances is key to producing top-notch electronic products. Let’s explore the world of PCB depaneling together.
What Exactly is PCB Depaneling and Why Is It Necessary?
As someone who has seen countless pcbs go from large panels to individual circuit boards, I can tell you that PCB depaneling is an absolutely critical step in the manufacturing process. Imagine a sheet of connected pcbs – that’s how they’re created in order to maximize efficiency. Depaneling is the process of removing those individual printed circuit board from the larger panel after all the components have been placed and solder has been applied, ready for use in electronic devices. This stage, sometimes also called singulation, is when we carefully separate the individual circuits.
The purpose of this process is simple: to transform a large, unwieldy panel of pcbs into the individual circuit boards that are essential for all kinds of electronic applications. These circuit boards are then ready to be integrated into various electronic assemblies. Without depaneling, we wouldn’t have the individual, functional boards needed for everything from smartphones to industrial equipment. As these pcbs are typically produced on a larger panel, depaneling is what makes each one a standalone product.
What are the Different Depaneling Methods Used in PCB Manufacturing?
Over the years, I’ve used and seen several methods of pcb depaneling in action. From the older techniques to state-of-the-art methods, each has its own strengths and weaknesses. In the early days, we relied on manual methods, which involved physically breaking apart the pcbs. While this was simple, it was also time-consuming and prone to errors. Then came the introduction of punch tooling, where a tool is used to create a separation through a specific die, creating a more uniform separation.
However, the real advancements came with the use of automated machinery. We started using router cutting, which employed a spinning tool used to cut along the designated separation line. This technique provided much better accuracy and efficiency compared to manual methods. Now, laser depaneling is becoming increasingly popular due to its precision and ability to cut complex shapes, and laser routing is rapidly becoming the most used cutting method. Each of these depaneling methods is still used today, and the choice depends on factors such as the type of PCB, desired precision, and throughput requirements.
How Does Router Cutting Compare to Other PCB Depaneling Techniques?
As someone who’s worked with both router cutting and other techniques, I’ve seen the pros and cons firsthand. Router cutting, a method I’ve used extensively, involves a spinning bit that precisely separates individual printed circuit boards. It’s a workhorse in the industry, offering a balance of speed and accuracy. However, it’s not perfect for every situation.
One of the main advantages of router cutting is its ability to handle various substrate materials and thicknesses. It’s reliable and has a relatively low cost of operation, making it a go-to for many pcb assembly plants. However, there are downsides. Router cutting introduces mechanical stress to the circuit boards, which can be a problem for sensitive components, particularly around the solder joints. This stress may also lead to micro-cracks or warping, especially on very thin pcbs. Additionally, the kerf width, or the amount of material removed by the cutting bit, can sometimes be quite large. This can limit how closely we can pack pcbs together on a panel, which increases waste. Comparing this to laser depaneling, the router technique is less precise, and introduces more stress.
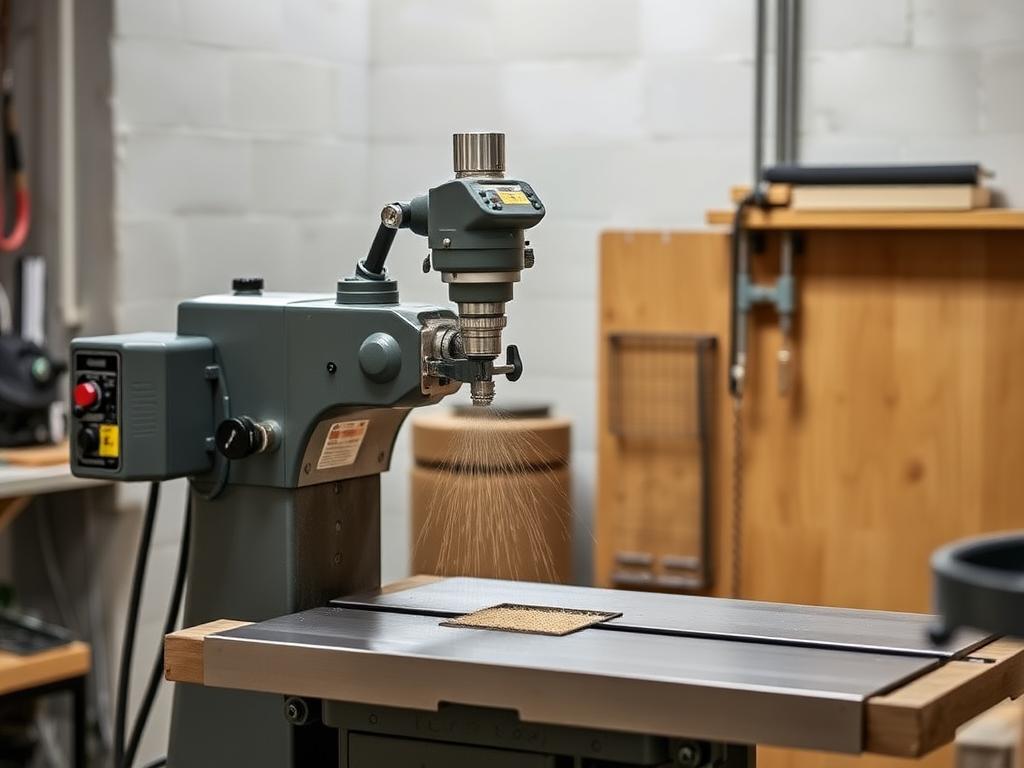
What is Laser Depaneling and How Does it Work?
Laser depaneling has always fascinated me, even after years of working in the PCB industry. It is a cutting system that has really changed the industry, using a focused laser source to separate individual circuits from the larger panel. Unlike mechanical cutting systems such as a router, laser cutting is a non-contact process, which greatly reduces the mechanical stress and the part induced stress on the circuit boards. This is particularly beneficial for sensitive components and high-density layouts.
The process involves directing a uv laser beam with extremely high energy density onto the pcb. The laser vaporizes the material along the cut line, creating a very narrow kerf width compared to traditional methods. The precision of the laser depaneling is extraordinary. It is possible to create very fine and intricate cuts and allows for complex shapes that cannot be achieved with a router, for instance. This method is great for intricate designs and especially beneficial when working with flex and rigid flex pcbs, which are more susceptible to mechanical damage. However, one drawback of laser depaneling is that it’s typically a slower process than router cutting, which can lead to lower throughput.
How is Laser Routing Revolutionizing the PCB Industry?
The introduction of laser routing has been transformative in the PCB manufacturing industry. It represents a significant step in the evolution of pcb depaneling and continues to impact all aspects of our work. It’s not just about cutting; it’s about precision, flexibility, and the ability to handle increasingly complex pcbs.
Laser routing offers several significant advantages compared to traditional methods. First and foremost, its precision is unparalleled, with minimal cut kerf, and it minimizes the risk of damage. This is particularly important when working with flex and rigid flex pcbs, which are often used in wearables and other sensitive applications. The non-contact nature of the laser means there’s no risk of stressing the delicate components and the extremely precise focused spot size ensures clean and accurate cuts, vital for the smaller components we use today. I’ve personally witnessed how laser routing has enabled us to produce incredibly complex board shapes and features that simply weren’t possible with traditional methods, making it an essential technology for advanced electronics. It is also far more flexible than router or punch, as the laser can be used to cut along any designed cut line, meaning new designs are easy to implement.
What Role Does Flex PCB Depaneling Play in Wearable Technology?
As someone deeply involved in the manufacturing process of flexible printed circuits, I’ve seen firsthand how crucial flex pcb depaneling plays, especially in the booming market of wearable technology. Flex pcbs and rigid flex pcbs are the cornerstone of many wearables and other applications that require miniaturization and flexibility. These thin and flexible circuit boards enable designers to create devices that conform to different shapes and offer greater freedom in the mechanical design of electronic devices.
Flex pcb depaneling plays a pivotal role in the manufacturing process of these flexible circuit boards. Wearable devices, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and other wearables, all rely on these flexible circuit boards. The process of flexible printed circuit board separation is particularly challenging because the flex materials are extremely sensitive to stress, and flex pcbs are even more susceptible to damage than rigid pcbs. Laser depaneling is often preferred for flex pcb separation due to its non-contact nature and precision. This method ensures that the pcbs are cleanly separated without introducing the mechanical stress or damage that may result in damage of the components or solder joints.
What is the future for PCB Depaneling systems?
The future of PCB depaneling is about automation, flexibility, and even greater precision, as I have seen the technology evolve over the years. The trend is towards creating more efficient, versatile, and intelligent depaneling systems. We are likely to see even more integration of laser routing technology, not just due to it’s greater precision, but also due to its flexibility for working with new designs. As pcbs become smaller and more complex, the need for precision laser pcb depaneling systems will grow significantly.
Beyond the laser source, automation is becoming key. This not only speeds up the depaneling process and reduces labor costs, but it also improves consistency and reliability. The pcb depaneling field will become more advanced, with depaneling systems integrating real-time monitoring and feedback systems to ensure quality, and adaptive systems that can adjust to variations in materials and designs automatically, minimizing waste and optimizing throughput. The future of pcb depaneling is a symphony of high-precision machines and intelligent control systems.
Why is precision so critical in the Depaneling Process?
In the world of pcb manufacturing, precision is not just a nice-to-have; it’s an absolute necessity. The depaneling process is the last step before these individual printed circuit boards are integrated into devices, and if this step is not done precisely, it can lead to problems down the line. I’ve seen firsthand how even small errors in depaneling can result in faulty products, delays, and additional costs.
The need for accuracy in depaneling stems from the delicate nature of modern circuit boards. These pcbs are densely packed with small components, and any unnecessary mechanical stress, or deviations in the cut line, can cause damage. Issues can range from micro-cracks in the substrate to damage to solder joints or the components themselves. The use of precise techniques, like laser routing, ensure that the pcbs are separated cleanly, minimizing the risk of defects. This level of precision ultimately contributes to higher quality products and greater reliability of the electronic devices.
What are the key components of an automated PCB depaneling system?
Having worked with automated depaneling systems for years, I’ve come to appreciate the importance of each component and how they all work together to ensure high-quality pcb separation. These complex systems are the backbone of efficient pcb manufacturing, and several key components are crucial for proper operation.
The most fundamental component of any automated system is the handling system that move the pcbs from the in-feed to the out-feed. This system ensures the correct positioning for the cutting systems, whether it is a router or a laser. The vision system, incorporating cameras and sophisticated software, allows for precise alignment of the cut line, ensuring consistency and accuracy. Another critical component is the control system, which manages the entire operation. This includes the computer controls, and the interface which can allow operators to monitor progress and make adjustments as needed. In a laser pcb depaneling system, the laser source itself is a critical component, responsible for the precise separation of the circuit boards.
Final Thoughts on Choosing the Right Cutting Systems
Throughout my career in the pcb manufacturing industry, I’ve learned that choosing the right cutting systems for depaneling is crucial. The process is not just about separating pcbs; it’s about efficiency, precision, and minimizing waste. We’ve gone from manually breaking pcbs apart to using sophisticated machinery, so the correct choice of depaneling method depends on the specific requirements of your product.
For example, if you’re working with flex pcbs or high-density layouts, you might be better served by the precision and low-stress nature of laser depaneling or laser routing. However, if you’re dealing with less sensitive designs and lower volumes, router cutting might be a cost-effective option. The key is to evaluate all your needs: the complexity of the pcb, the required throughput, and sensitivity to mechanical stress, and so on. This will ensure that you choose the best possible cutting method for your specific application.
Remember, the goal of depaneling is to produce high-quality circuit boards that meet all specifications and requirements. As the technology continues to advance, I’m confident that the future of depaneling will lead to ever greater levels of efficiency and precision. At PCB Depaneling, we are dedicated to providing the best technology for your business, from PCB Router Machines, to V-Groove Depaneling, and PCB Laser Depaneling systems. We offer solutions from manual to laser, and we can advise you on the best method to suit your manufacturing requirements. Don’t hesitate to contact our sales team for a quote, or if you require assistance with PCB depaneling.
- To see the full range of our PCB Router Machine, visit our product page.
- If you would like to know more about V-Groove Depaneling, we have a complete list of products here.
- For those interested in the latest in PCB Laser Depaneling see our page
- You may be interested in our PCB/FPC Punching Machine solutions that we offer here.
- To see our entire range of Automatic Equipment, please click here
- And for a complete list of Accessories, see our page.
FAQs
How can I minimize stress on my pcbs during depaneling? Choosing a non-contact method such as laser depaneling is the most effective way to minimize stress on your pcbs during the depaneling process. Laser routing avoids the mechanical stress that router and punch methods can impose.
What is the best cutting method for flex pcbs? Laser depaneling is generally considered the best method for flex pcbs and rigid flex pcbs. Its precision and minimal mechanical stress ensures that delicate boards are separated cleanly and without damage.
What’s the difference between router cutting and laser routing? Router cutting uses a spinning bit to separate pcbs, which creates mechanical stress, and produces a wider kerf width. Laser routing, on the other hand, uses a focused laser beam. It is a non-contact process, which eliminates mechanical stress and provides much more accurate cuts with a narrower kerf width.
What factors should I consider when choosing a depaneling system? When choosing a depaneling system, consider factors such as the types of pcbs you’re working with, desired precision, throughput, cut kerf, and the level of automation you require.
Can you integrate the depaneling systems into a full production line? Yes, all the depaneling systems that we supply can be integrated into a full production line, with full automation. We offer solutions for in-line SMT production, and many other options. See our SMT whole line equipment page for more details.
Summary
- PCB depaneling is essential for separating individual circuit boards from larger panels, and is a critical step in the manufacturing process.
- Different depaneling methods exist, including manual, punch, router cutting, and laser depaneling, each with its own pros and cons.
- Router cutting is a common method but can induce mechanical stress and is not suitable for all designs.
- Laser depaneling provides unmatched precision and minimizes stress, making it ideal for flex pcbs, and rigid flex pcbs, along with complex designs.
- Laser routing is revolutionizing the industry with its high precision and ability to cut complex shapes.
- Flex pcb depaneling is vital for the manufacturing process of wearable technologies, and other applications that require flexible boards.
- The future of depaneling involves greater automation, precision, and real-time monitoring.
- Choosing the right depaneling system depends on the specific requirements of the pcb design and application.
- Precision is key to ensure the high quality of the final product and avoiding any damage during the process of removing the individual circuits.